-
摘要:目的
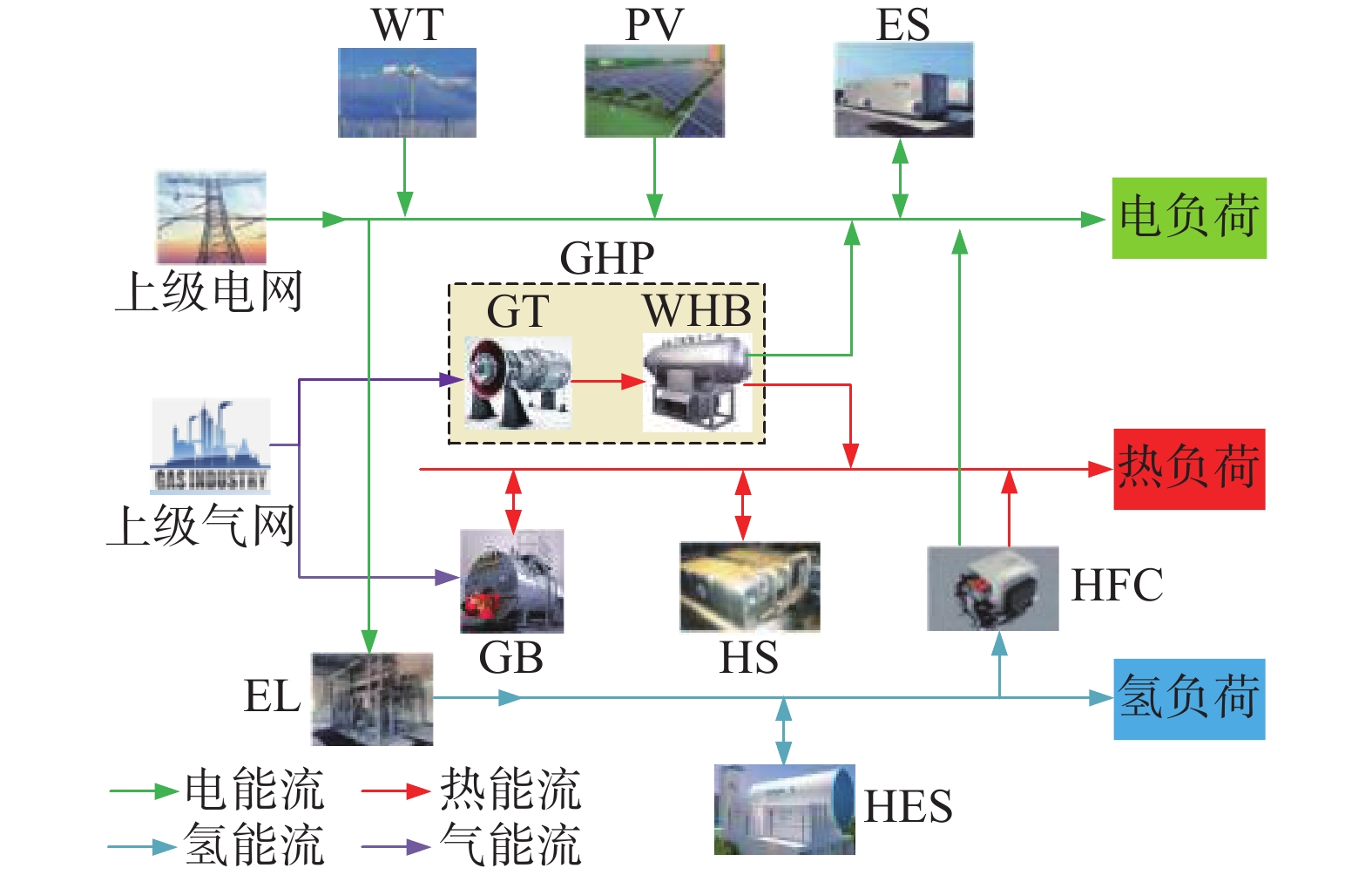
随着能源领域的改革的不断深入,能源与交通的融合是港口多能流的未来发展趋势。引入多能柔性负荷的需求响应机制和电解槽变载启停特性已经成为港口综合能源系统(PIES)发展的必然趋势。
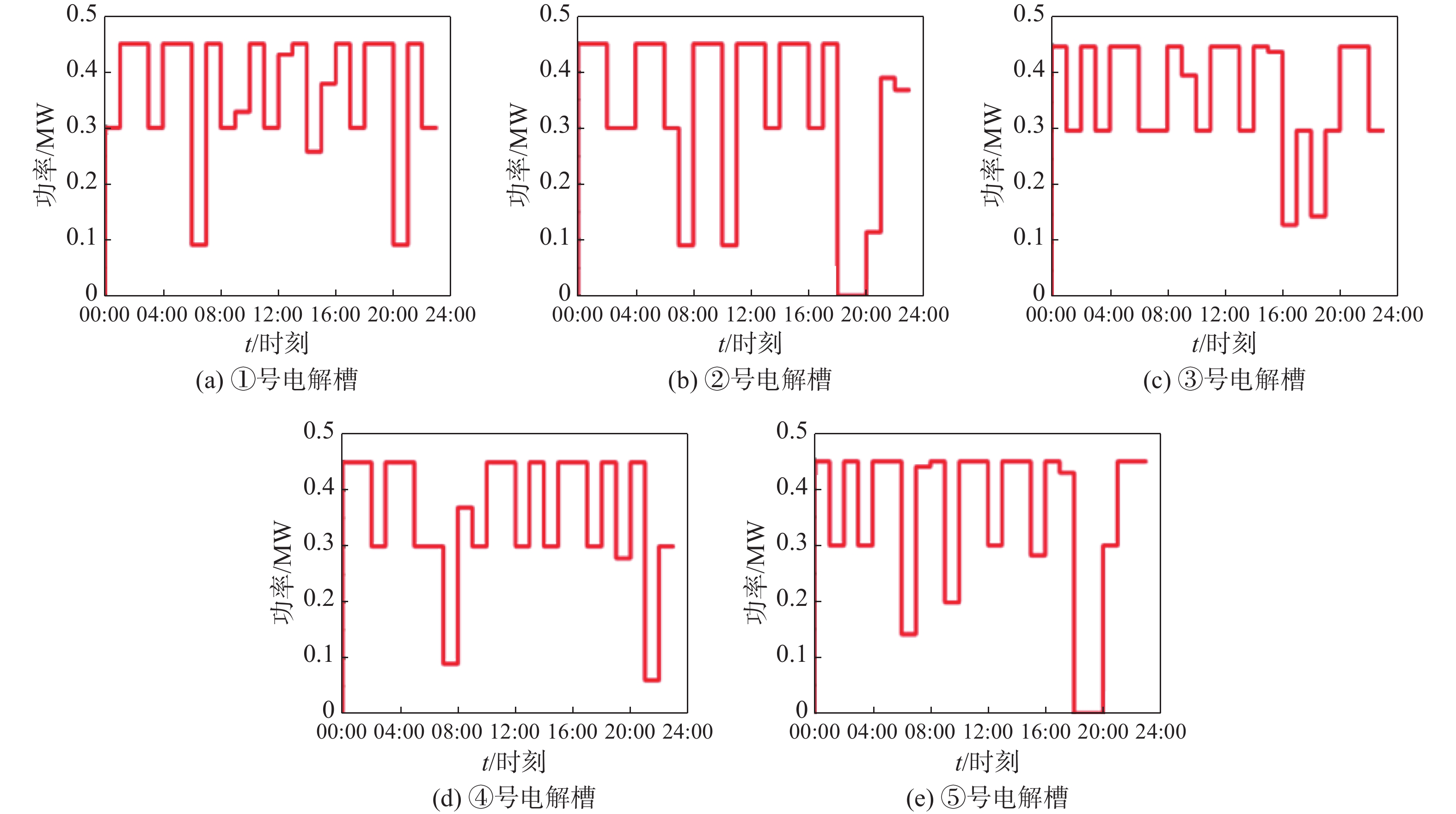
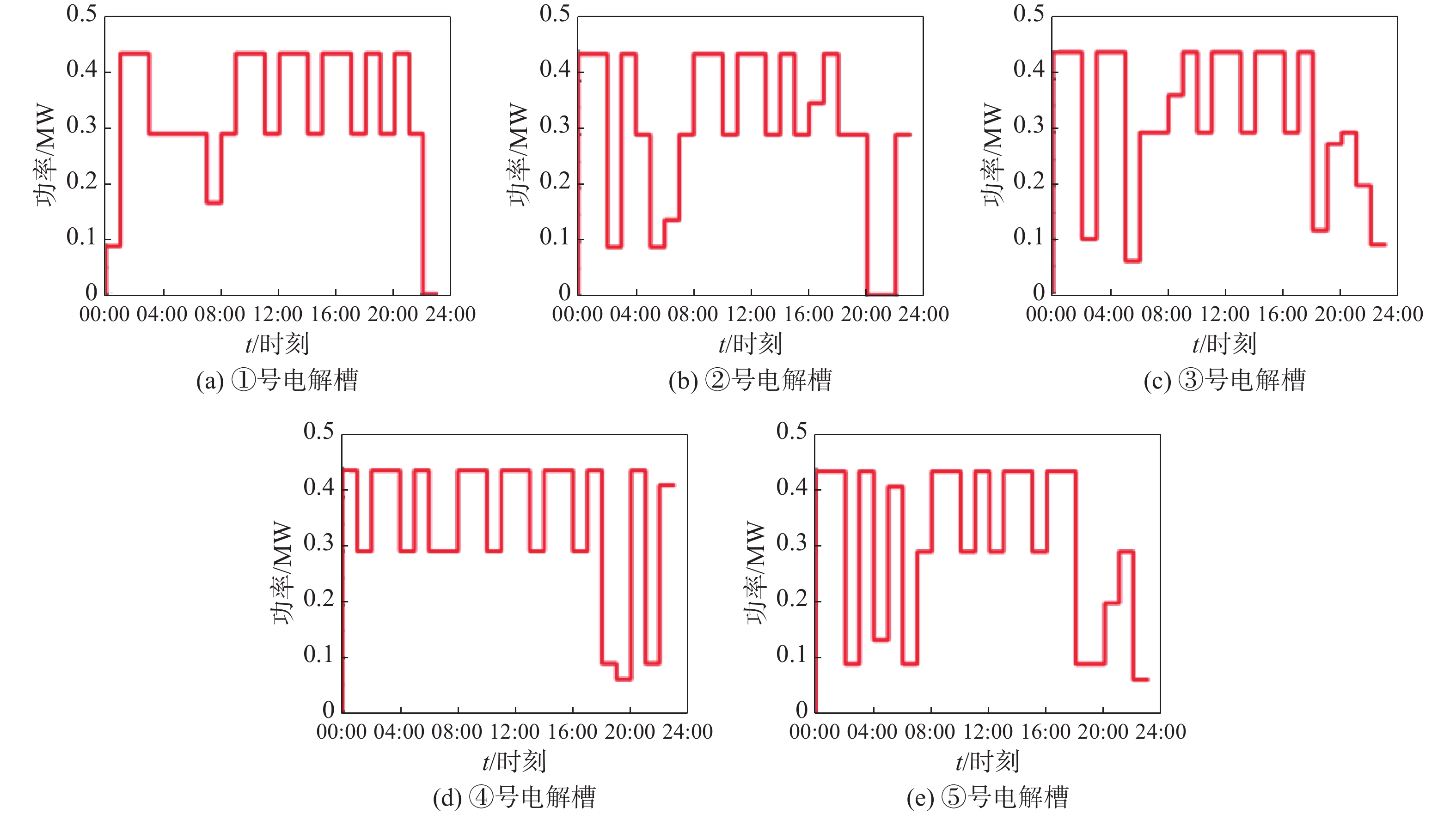
方法基于PIES中多能流的耦合特性,同时根据港口用户侧的用能特性,将电、热、氢3种柔性负荷划分为可平移负荷、可转移负荷以及可削减负荷,建立了考虑电、热、氢负荷需求响应的PIES运行优化模型。在此模型考虑电解槽的运行特性,并提出多堆电解槽组合运行,并以经济成本为优化目标,并采用Yalmip工具箱和Gurobi求解器求解。求解得到负荷响应前后各能源网络的优化结果。
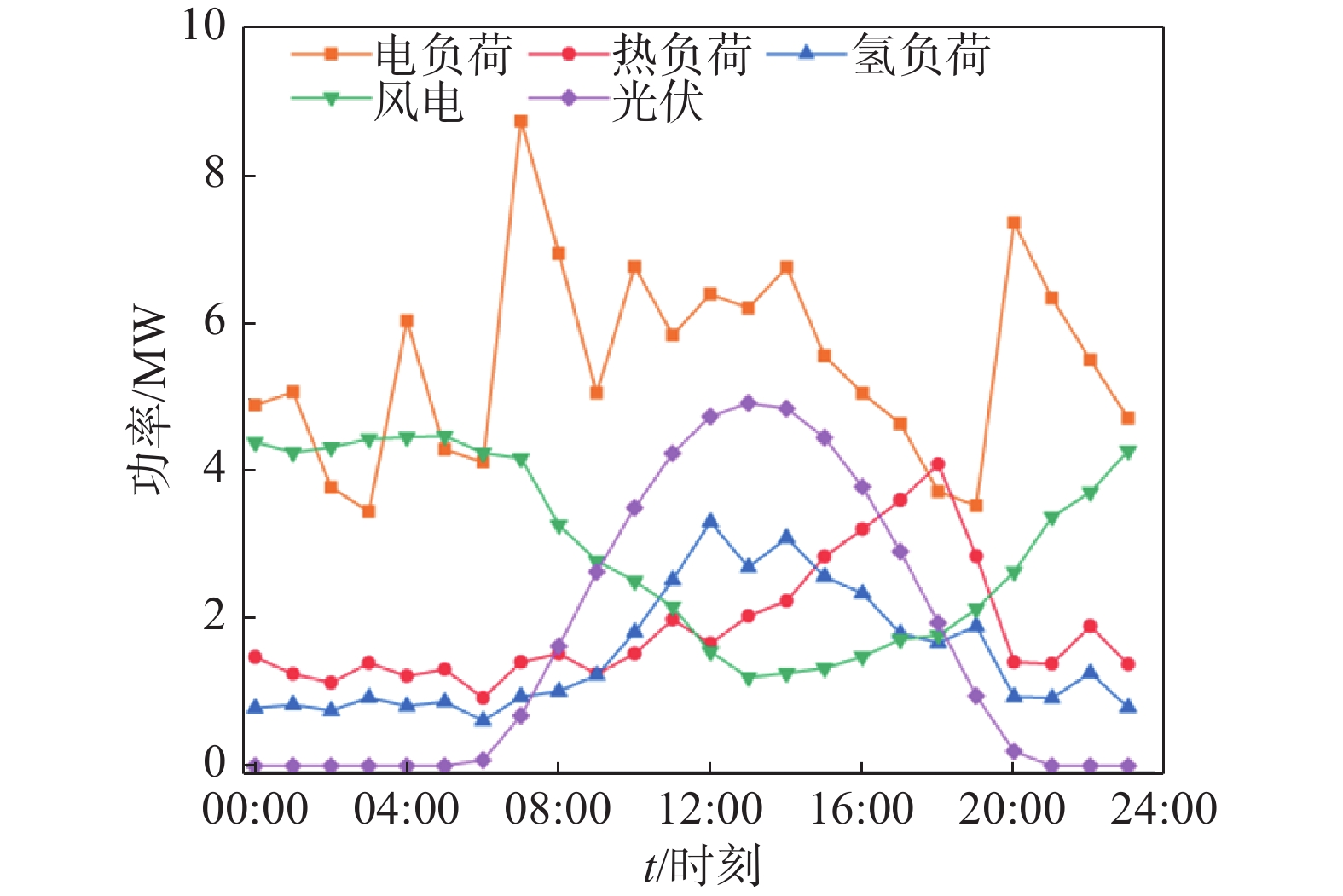
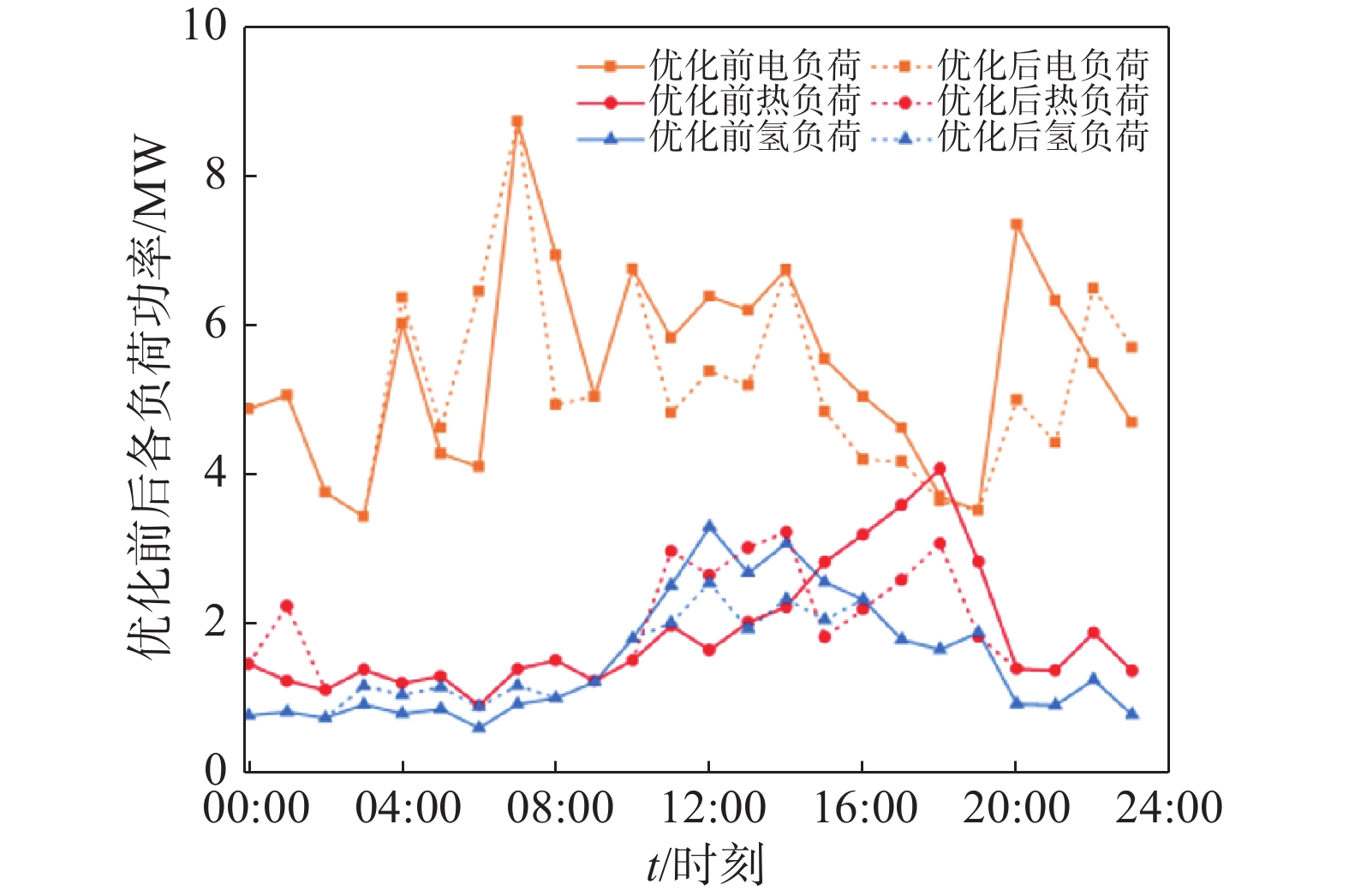
结果算例结果表明,引入柔性负荷的港口综合能源系统实现了多能负荷的削峰填谷,使得用能曲线更加平稳,降低了2.28%的总成本,有利于提高经济效益。但由于风光资源的不确定性,柔性负荷会对电解槽运行阵列产生不定的影响。
结论验证了结合柔性负荷和电解槽多工况组合运行所建的港口综合能源系统模型的可行性和实用性。
Abstract:ObjectiveAs the reform in the energy sector continues to deepen, the integration of energy and transportation is the future development trend of multi-energy flows in ports. The introduction of demand response mechanisms for multi-energy flexible loads and the variable load start-stop characteristics of electrolyzers have become an inevitable trend in the development of port integrated energy systems (PIES).
MethodBased on the coupling characteristics of multi-energy flows in PIES and in accordance with the energy consumption characteristics of port users, three flexible loads of electricity, heat and hydrogen were classified into shiftable loads, transferable loads and reducible loads. An operation optimization model of PIES considering the demand response of electricity, heat and hydrogen loads was established. In this model, the operating characteristics of electrolyzers were considered, and the combined operation of multi-stack electrolyzers was proposed. With economic cost as the optimization goal, Yalmip toolbox and Gurobi solver were used to solve the model. Therefore, optimal results of each energy network before and after load response were obtained.
ResultThe results of the case study show that the introduction of flexible loads in the port's integrated energy system has achieved peak shaving and valley filling of multi-energy loads, making the energy consumption curve more stable and reducing the total cost by 2.28%, which is beneficial to improving economic benefits. However, due to the uncertainty of wind and solar resources, flexible loads may have an uncertain impact on the operation array of electrolyzers.
ConclusionThe feasibility and practicality of the port integrated energy system model established by combining flexible loads and multi-operation mode combinations of electrolyzers have been verified.
-
表 1 能源耦合设备参数
Table 1 Parameters of energy coupling equipment
设备类型 能量转换效率/% 容量/MW 爬坡约束/% CHP 92 5 20 HFC 83 0.5 20 GB 95 0.8 20 表 2 储能设备参数
Table 2 Parameters of energy storage equipment
设备类型 容量/MW 容量下限/% 容量下限/% ES 15 20 90 HS 10 20 90 HES 10 20 90 表 3 设备运维成本系数
Table 3 Cost coefficient of equipment operation and maintenance
设备类型 运维成本系数/[元·(MWh)−1] WT 10 PV 20 CHP 45 GB 45 EL 35 HFC 25 ES 18 HS 15 HES 16 表 4 柔性负荷参数(1)
Table 4 Flexible load parameters (1)
类型 td/h tsf-~tsf+ cshiftcost/[元·(MWh)−1] 可平移电负荷1 2 2:00-19:00 200 可平移电负荷2 2 9:00-23:00 200 可平移热负荷 5 1:00-14:00 100 可平移氢负荷 5 2:00-23:00 100 表 5 柔性负荷参数(2)
Table 5 Flexible load parameters (2)
类型 Ttranmin/h Ptranmin~Ptranmax/MW tsf-~tsf+ ctrancost/[元·(MWh)−1] 可转移电负荷 3 0.35~0.87 1:00-14:00 100 可转移氢负荷 2 0.04~0.17 2:00-23:00 100 表 6 柔性负荷参数(3)
Table 6 Flexible load parameters (3)
类型 Tcutmin/h Tcutmax/h Nmax/次 ccutcost/[元·(MWh)−1] 可削减电负荷 2 5 8 400 可削减热负荷 2 5 8 200 表 7 系统运行成本结果
Table 7 Result of system operating cost
元 方案 购能成本 弃风弃光成本 运维成本 补偿成本 总成本 1 24 732.93 0 2 103.20 0 26 836.13 2 20 331.46 0 2 020.17 3 872.70 26 224.33 -
[1] 袁裕鹏, 许朝远, 李娜, 等. 港口多能源融合系统综述 [J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(4): 83-103. DOI: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.04.007. YUAN Y P, XU C Y, LI N, et al. Review on multi-energy integration systems in ports [J]. Journal of traffic and transportation engineering, 2024, 24(4): 83-103. DOI: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.04.007.
[2] 唐道贵, 柯耀, 张乾能, 等. 港口实景下大型风电机组工程化设计分析 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2024, 11(1): 64-72. DOI: 10.16516/j.ceec.2024.1.07. TANG D G, KE Y, ZHANG Q N, et al. Engineering design analysis of large-scale wind turbine in a port [J]. Southern energy construction, 2024, 11(1): 64-72. DOI: 10.16516/j.ceec.2024.1.07.
[3] 王晴勤, 温国标. 基于交能融合的分布式海上风电选址与布置 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2024, 11(2): 59-67. DOI: 10.16516/j.ceec.2024.2.06. WANG Q Q, WEN G B. Site selection and layout of distributed offshore wind power based on energy and transportation integration [J]. Southern energy construction, 2024, 11(2): 59-67. DOI: 10.16516/j.ceec.2024.2.06.
[4] 侯慧, 谢应彪, 赵波, 等. 能源与交通耦合的港口多能微网优化调度综述 [J]. 电力自动化设备, 2025, 45(3): 50-63. DOI: 10.16081/j.epae.202412035. HOU H, XIE Y B, ZHAO B, et al. Review of optimal scheduling for port multi-energy microgrid with energy and transportation coupling [J]. Electric power automation equipment, 2025, 45(3): 50-63. DOI: 10.16081/j.epae.202412035.
[5] 韩子娇. 风-光-氢耦合系统协调控制与运行经济性研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2024. DOI: 10.27322/d.cnki.gsgyu.2024.000064. HAN Z J. Coordinated control and operation economy of wind-photovoltaic-hydrogen coupled system [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2024. DOI: 10.27322/d.cnki.gsgyu.2024.000064.
[6] 徐晓健, 刘大壮, 王霓, 等. “风光氢储”多能源融合系统港船综合应用适应性研究 [J]. 交通节能与环保, 2024, 20(3): 55-61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6478.2024.03.012. XU X J, LIU D Z, WANG N, et al. Adaptability study of "wind-solar-hydrogen-energy storage" in port-ship multi-energy integration system [J]. Transport energy conservation & environmental protection, 2024, 20(3): 55-61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6478.2024.03.012.
[7] 杨瑞, 李响, 周垣孜, 等. 港船多能源融合技术体系构建与运行模式研究 [J]. 交通节能与环保, 2024, 20(2): 39-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6478.2024.02.008. YANG R, LI X, ZHOU Y Z, et al. Analysis of construction and operating mode of multi energy integration technology system for port ship [J]. Transport energy conservation & environmental protection, 2024, 20(2): 39-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6478.2024.02.008.
[8] 张杰, 罗雪鹏. 液氢制-储-运-加关键技术发展现状及展望 [J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 888-898. DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24019. ZHANG J, LUO X P. Development Status and Prospect of Key Technologies for Liquid Hydrogen Production-Storage-Transportation-Refueling [J]. Power generation technology, 2024, 45(5): 888-898. DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24019.
[9] 赵景茜, 米翰宁, 程昊文, 等. 考虑岸电负荷弹性的港区综合能源系统规划模型与方法 [J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2021, 55(12): 1577-1585. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2021.293. ZHAO J Q, MI H N, CHENG H W, et al. A planning model and method for an integrated port energy system considering shore power load flexibility [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(12): 1577-1585. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2021.293.
[10] 周思怡, 杨欢红, 黄文焘, 等. 集装箱港口综合能源系统日前-日内两阶段滚动优化调度 [J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024, 58(9): 1357-1369. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.016. ZHOU S Y, YANG H H, HUANG W T, et al. Two-stage day-ahead and intra-day rolling optimization scheduling of container integrated port energy system [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2024, 58(9): 1357-1369. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.016.
[11] 张紫阳, 周雪松, 李佳琪, 等. 考虑电转气和冷藏集装箱的港口综合能源系统优化运行 [J/OL]. 天津理工大学学报, 2024: 1-8(2024-12-04) [2025-04-28]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1374.N.20241204.1011.002.html. ZHANG Z Y, ZHOU X S, LI J Q, et al. Optimization operation of port integrated energy system considering power to gas and refrigerated containers [J/OL]. Journal of Tianjin University of Technology, 2024: 1-8(2024-12-04) [2025-04-28]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1374.N.20241204.1011.002.html.
[12] 方斯顿, 赵常宏, 丁肇豪, 等. 面向碳中和的港口综合能源系统(一): 典型系统结构与关键问题 [J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(1): 114-134. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.212120. FANG S D, ZHAO C H, DING Z H, et al. Port integrated energy systems toward carbon neutrality (part I): typical topology and key problems [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(1): 114-134. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.212120.
[13] 郭燚, 周淼, 韩冰. 考虑氢能利用的港口综合能源系统低碳经济优化调度 [J/OL]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2024: 1-10 (2024-09-04) [2025-04-28]. https://doi.org/10.19635/j.cnki.csu-epsa.001519. GUO Y, ZHOU M, HAN B. Low-carbon economic optimal dispatch of integrated port energy system considering utilization of hydrogen energy [J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2024: 1-10 (2024-09-04) [2025-04-28]. https://doi.org/10.19635/j.cnki.csu-epsa.001519.
[14] 赵东, 何山, 韩璐 , 等. 离网型制氢系统典型短路故障分析及协同保护 [J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52(21): 60-70. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.240057. ZHAO D, HE S, HAN L, et al. Typical short-circuit fault analysis and cooperative protection of an off-grid hydrogen production system [J]. Power system protection and control, 2024, 52(21): 60-70 . DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.240057.
[15] 杨胜, 樊艳芳, 侯俊杰,等. 可再生能源ALK-PEM联合制氢系统多时间尺度优化运行策略 [J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2025, 53(3): 68-80. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.240512. YANG S, FAN Y F, HOU J J, et al. Multi-time scale optimization strategy of a renewable energy ALK-PEM combined hydrogen production system [J]. Power system protection and control, 2025, 53(3): 68-80. DOI: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.240512.
[16] 邓杰, 姜飞, 王文烨, 等. 考虑电热柔性负荷与氢能精细化建模的综合能源系统低碳运行 [J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46(5): 1692-1702. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.1373. DENG J, JIANG F, WANG W Y, et al. Low-carbon optimized operation of integrated energy system considering electric-heat flexible load and hydrogen energy refined modeling [J]. Power system technology, 2022, 46(5): 1692-1702. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.1373.
[17] 朱兰, 王吉, 唐陇军, 等. 计及电转气精细化模型的综合能源系统鲁棒随机优化调度 [J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(1): 116-125. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2018.1895. ZHU L, WANG J, TANG L J, et al. Robust stochastic optimal dispatching of integrated energy systems considering refined power-to-gas model [J]. Power system technology, 2019, 43(1): 116-125. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2018.1895.
[18] 田雪沁, 冯亚杰, 袁铁江, 等. 考虑电氢负荷柔性的多堆电解槽优化运行 [J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49(1): 84-92. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2023.1885. TIAN X Q, FENG Y J, YUAN T J, et al. Optimal operation of multi alkaline electrolyzers considering flexible electrical and hydrogen load [J]. Power system technology, 2025, 49(1): 84-92. DOI: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2023.1885.
[19] 胡俊杰, 童宇轩, 刘雪涛, 等. 计及精细化氢能利用的综合能源系统多时间尺度鲁棒优化策略 [J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(5): 1419-1435. DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.222335. HU J J, TONG Y X, LIU X T, et al. Multi-time-scale robust optimization strategy for integrated energy system considering the refinement of hydrogen energy use [J]. Transactions of China electrotechnical society, 2024, 39(5): 1419-1435. DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.222335.
[20] VARELA C, MOSTAFA M, ZONDERVAN E. Modeling alkaline water electrolysis for power-to-x applications: a scheduling approach [J]. International journal of hydrogen energy, 2021, 46(14): 9303-9313. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.12.111.
[21] 曲琪, 滕菲, 郭禹辛, 等. 考虑算力需求的港口综合能源系统分布式能源管理 [J]. 综合智慧能源, 2025, 47(1): 42-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0706.2025.01.006. QU Q, TENG F, GUO Y X, et al. Distributed energy management of port integrated energy system considering computing power demands [J]. Integrated intelligent energy, 2025, 47(1): 42-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0706.2025.01.006.
[22] 伏绍鑫, 张路, 唐翰峰, 等. 考虑柔性电热负荷的区域综合能源系统低碳经济调度 [J]. 电力科技与环保, 2023, 39(5): 417-428. DOI: 10.19944/j.eplep.1674-8069.2023.05.007. FU S X, ZHANG L, TANG H F, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of community integrated energy system consid-ering flexible electric heating load [J]. Electric power technology and environmental protection, 2023, 39(5): 417-428. DOI: 10.19944/j.eplep.1674-8069.2023.05.007.
[23] 薛开阳, 楚瀛, 凌梓, 等. 考虑柔性负荷的综合能源系统低碳经济优化调度 [J]. 可再生能源, 2019, 37(8): 1206-1213. DOI: 10.13941/j.cnki.21-1469/tk.2019.08.016. XUE K Y, CHU Y, LING Z, et al. Low-carbon economic optimal dispatch of integrated energy system considering flexible load [J]. Renewable energy resources, 2019, 37(8): 1206-1213. DOI: 10.13941/j.cnki.21-1469/tk.2019.08.016.
[24] 刘蓉晖, 李子林, 杨秀, 等. 考虑用户侧柔性负荷的社区综合能源系统日前优化调度 [J]. 太阳能学报, 2019, 40(10): 2842-2850. DOI: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.2019.10.018. LIU R H, LI Z L, YANG X, et al. Optimal dispatch of community integrated energy system considering user-side flexible load [J]. Acta energiae solaris sinica, 2019, 40(10): 2842-2850. DOI: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.2019.10.018.




 下载:
下载: