-
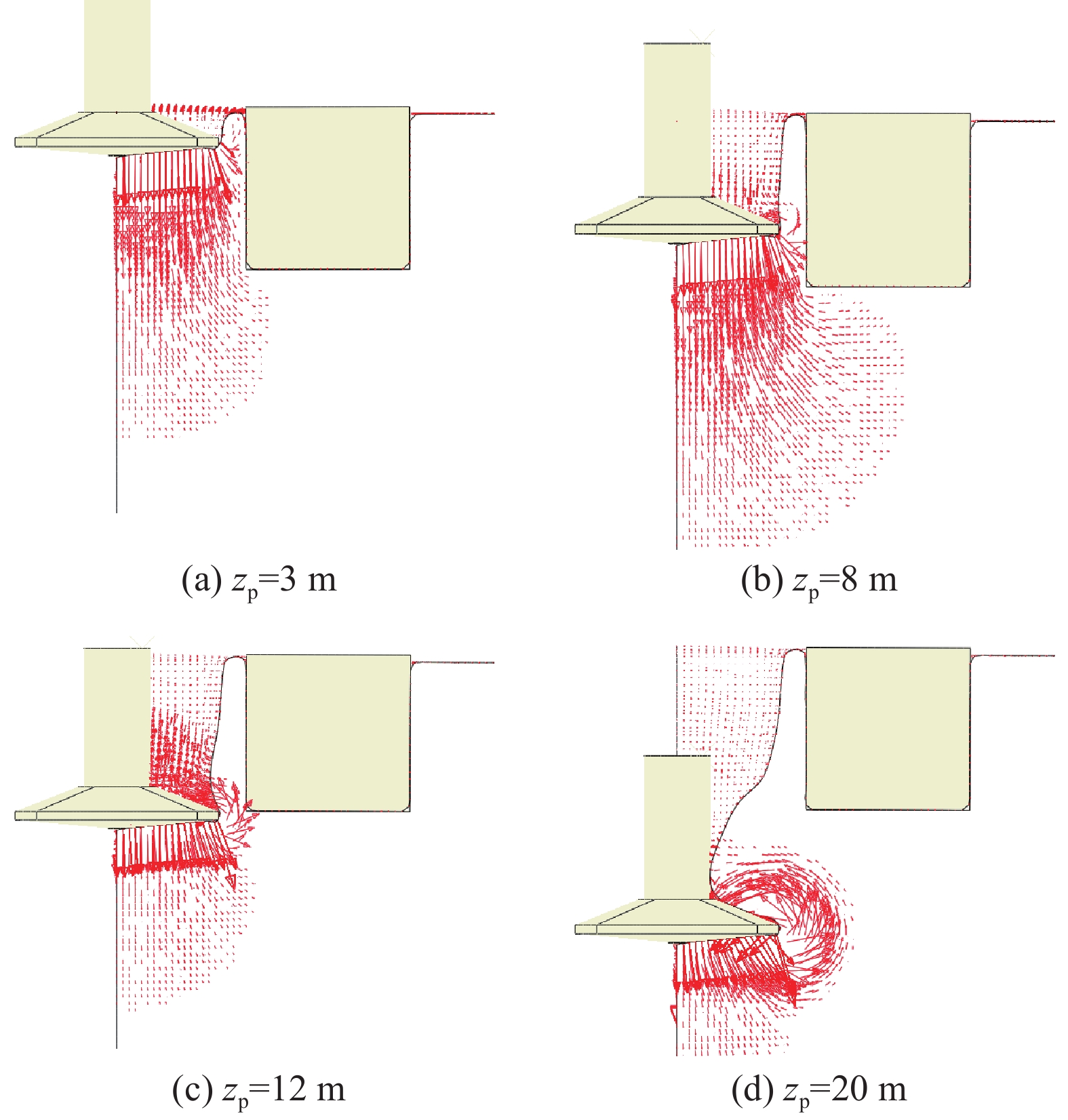
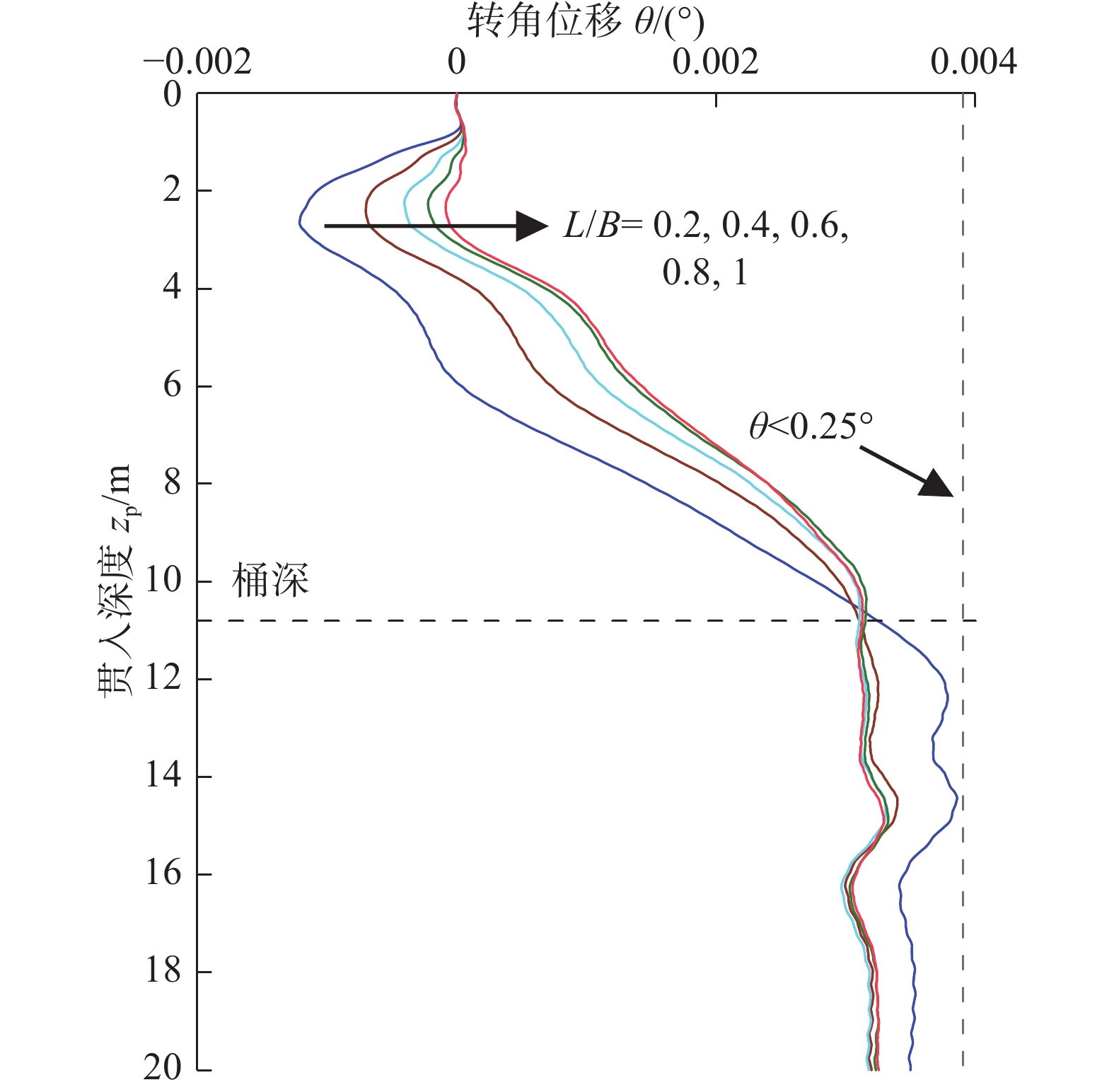
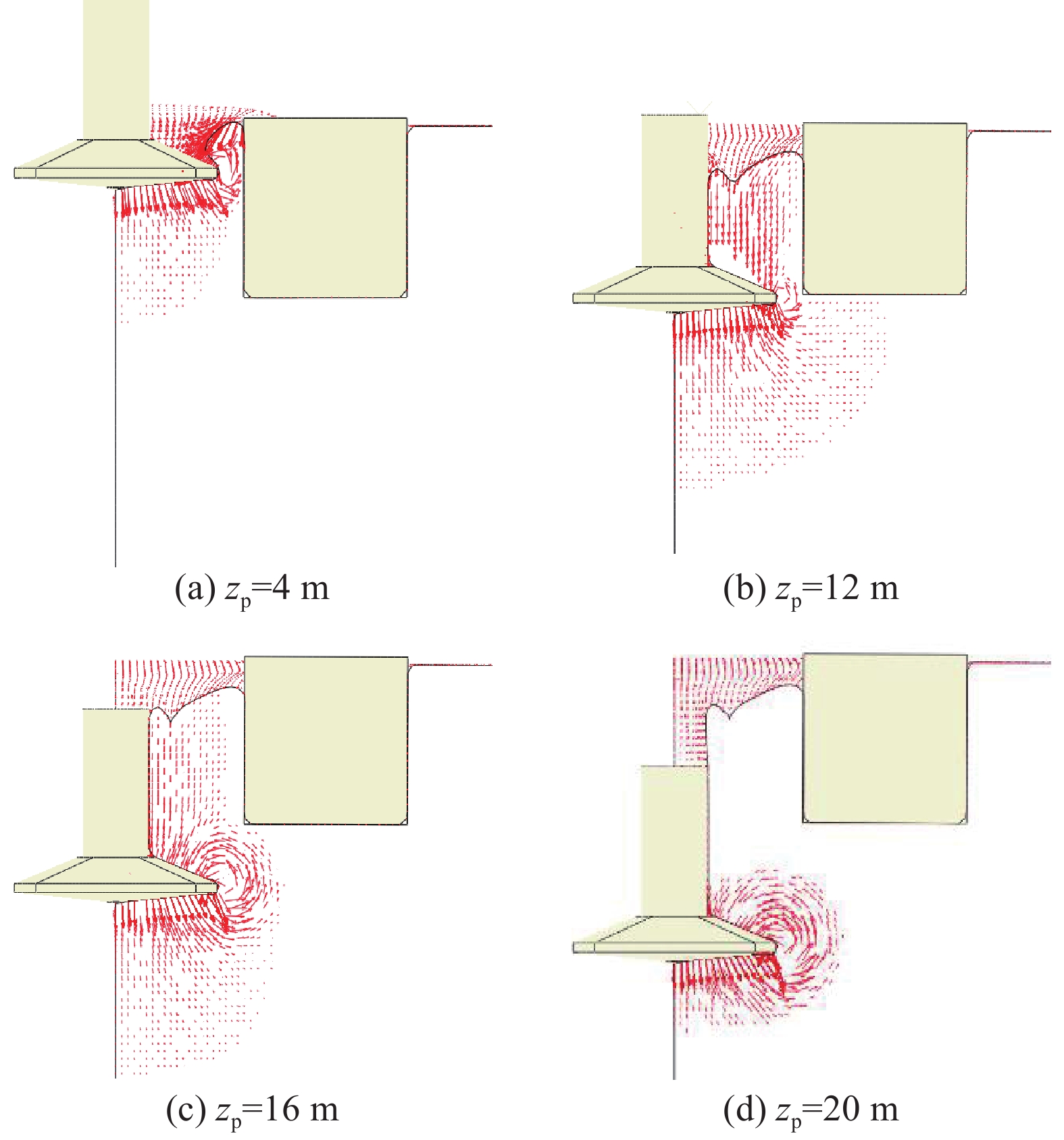
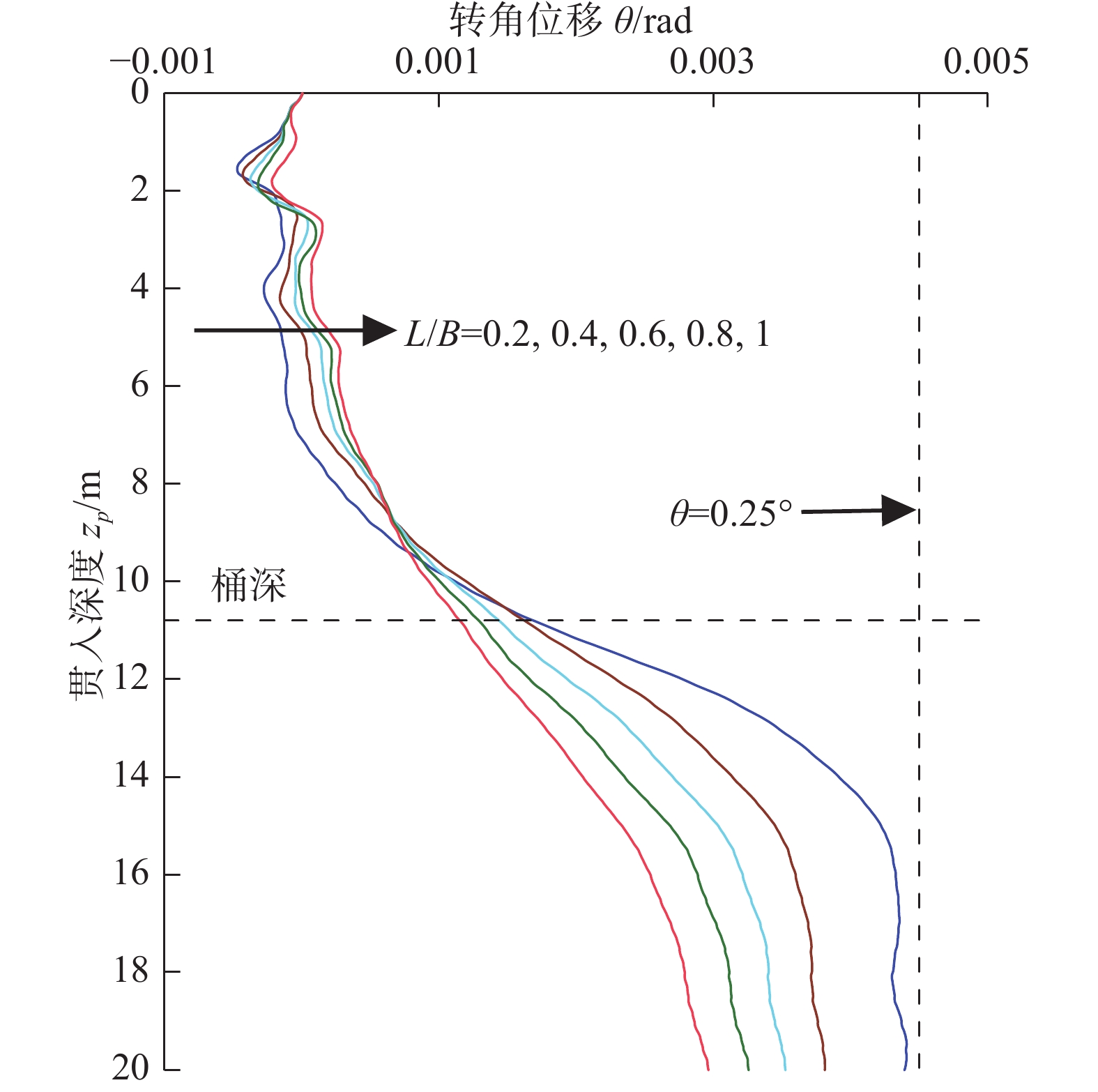
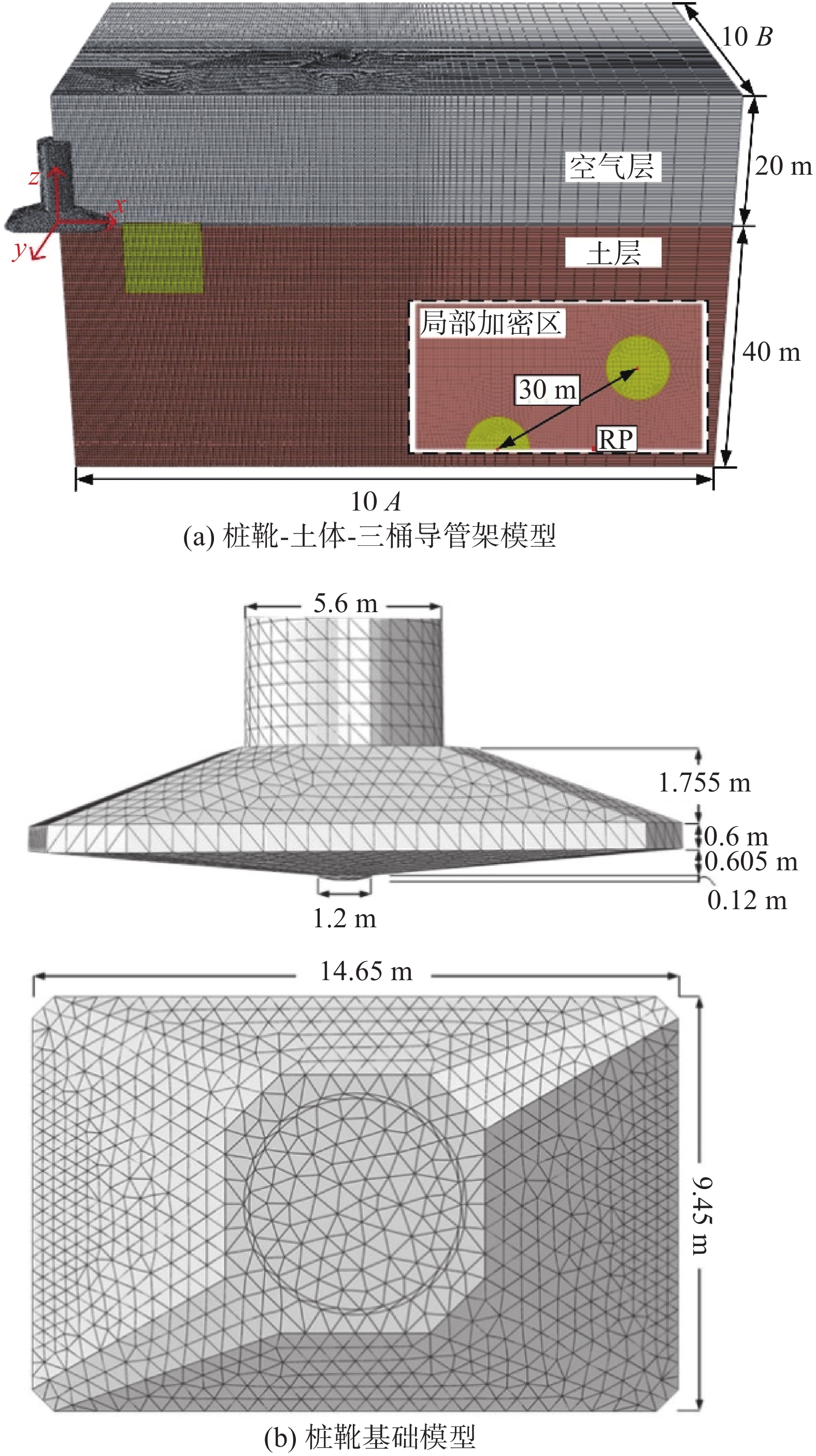
摘要:目的 移动式平台进场安装海上风机的插拔桩施工过程风险大,易影响邻近基础结构的工作性能,甚至导致其失稳破坏。方法 为厘清桩靴插拔过程对临近基础的影响机理,文章针对类矩形桩靴,采用CEL大变形方法,开展了其在均质和非均质黏土中插拔过程模拟,重点分析了插桩过程对邻近导管架基础产生的附加倾覆角演变机理;并基于大变形模拟结果,利用小变形进一步研究了桩靴拔出后土体软化效应对邻近桶各向极限承载力的影响。结果 研究结果表明,在桩靴挤土作用下,三桶导管架基础均会发生先顺后逆的转动位移,且随着净间距的增加而逐渐减小。同时,挤土导致的土体软化会使邻近桶各向承载力降低。结论 受插拔桩靴的影响,非均质土中的三桶导管架的倾覆角度更大,所对应的贯入深度更深。插拔桩靴所造成的软化区域影响范围在均质黏土中水平方向延伸较大,深度方向较小。在均质黏土中,平均强度损失较小,三桶导管架的水平向、转角向的承载力损失较少。在均质和非均质黏土中,竖向承载力折减明显,最大折减系数可达0.72。Abstract:Introduction The construction process of pile insertion and removal for installing offshore wind turbines on mobile platforms is risky, which can easily affect the working performance of adjacent infrastructure, and even lead to its instability and failure.Method In order to clarify the mechanism of the influence of pile shoe insertion and removal on adjacent foundation, this paper used CEL large deformation method to simulate the insertion and removal process of similar rectangular pile shoe in homogeneous and heterogeneous clay, and focused on the analysis of the evolution mechanism of additional overturning angle caused by pile insertion process on adjacent jacket foundation; based on the simulation results of large deformation, the influence of soil softening effect on the ultimate bearing capacity of adjacent buckets after pile shoe removal was further studied by using small deformation.Result The results show that under the action of pile shoe compaction, the rotational displacement of the three-cylinder jacket foundation will take place, and it will decrease gradually with the increase of net spacing. At the same time, the soil softening caused by compaction will reduce the bearing capacity of adjacent cylinder.Conclusion The overturning angle of three-cylinder jacket in heterogeneous soil is larger and the corresponding penetration depth is deeper due to the influence of pile shoe insertion and removal. The affected area of softening area caused by pile shoe insertion and removal is larger in horizontal direction and smaller in depth direction in homogeneous clay. In homogeneous clay, the average strength loss is small, and the horizontal and angular bearing capacity loss of the three-cylinder jacket is small. In homogeneous and heterogeneous clays, the vertical bearing capacity is reduced obviously, and the maximum reduction factor can reach 0.72.
-
Keywords:
- pile shoe /
- large deformation /
- small deformation /
- softening effect /
- overturning /
- bearing capacity
-
表 1 土层材料特性
Table 1 Soil properties
土体 性质 su0/kPa γ/(kN·m−3) Soil#1 均质黏土 20 6 Soil#2 非均质黏土 1+z 6 表 2 小变形验证结果
Table 2 Validation results of small deformation
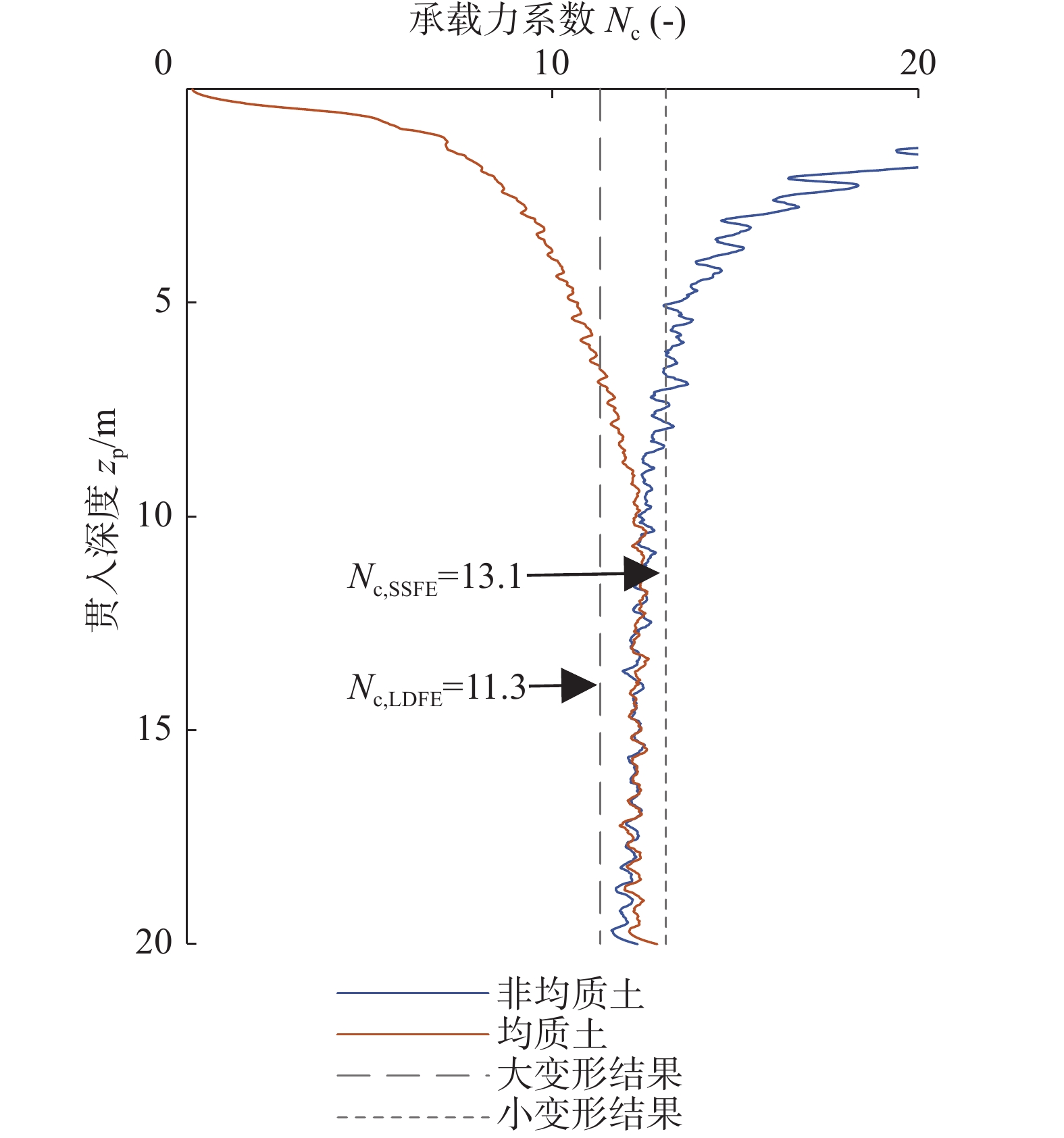
文献 承载力系数 水平向/NcH 弯矩向/NcM 竖向/NcV Liu等[23] 4.50 1.63 10.75 本模型 4.37 1.51 10.55 误差/% 2.90 7.85 1.90 表 3 土体部分软化区域和软化程度
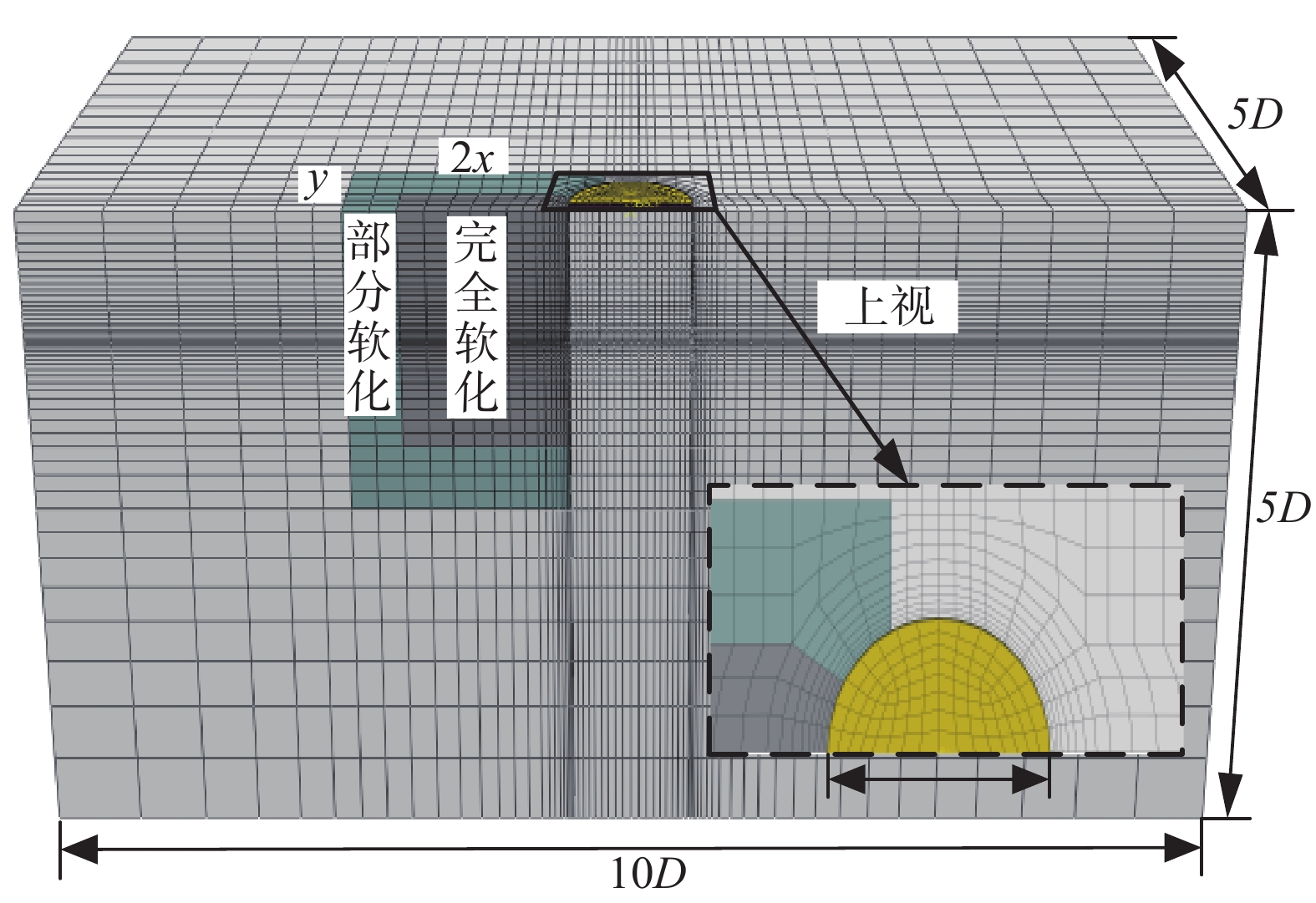
Table 3 Softening zone and degree of soil
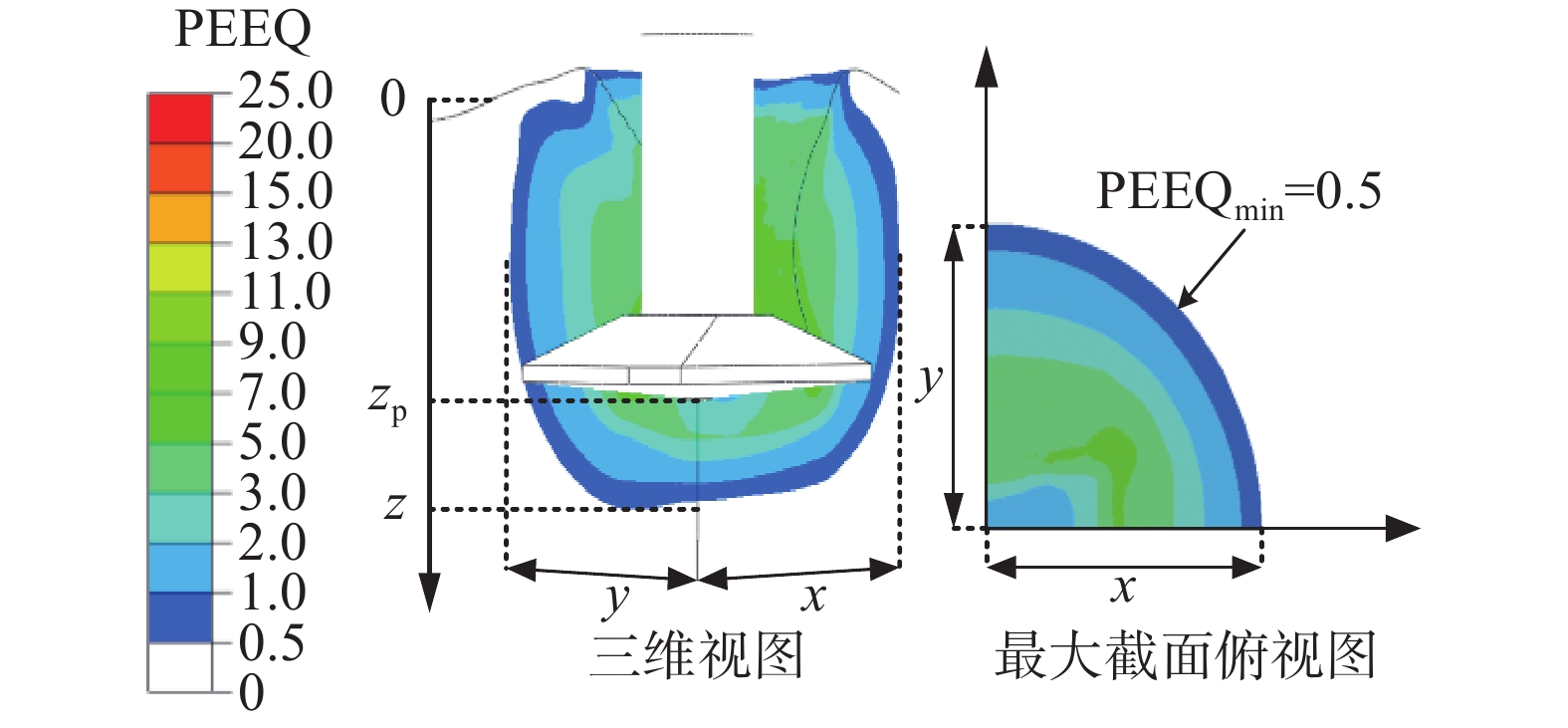
土体 软化程度 软化区域 备注 PEEQav βav x/B y/B (z−zp)/B soil#1 5.75 0.38 1.3 1.2 0.6 zp = 20 m Soil#2 7.75 0.32 1.5 1.5 0.3 表 4 邻近桶各向单轴极限承载力及折减系数
Table 4 Uniaxial ultimate bearing capacity and reduction factor near each cylinder
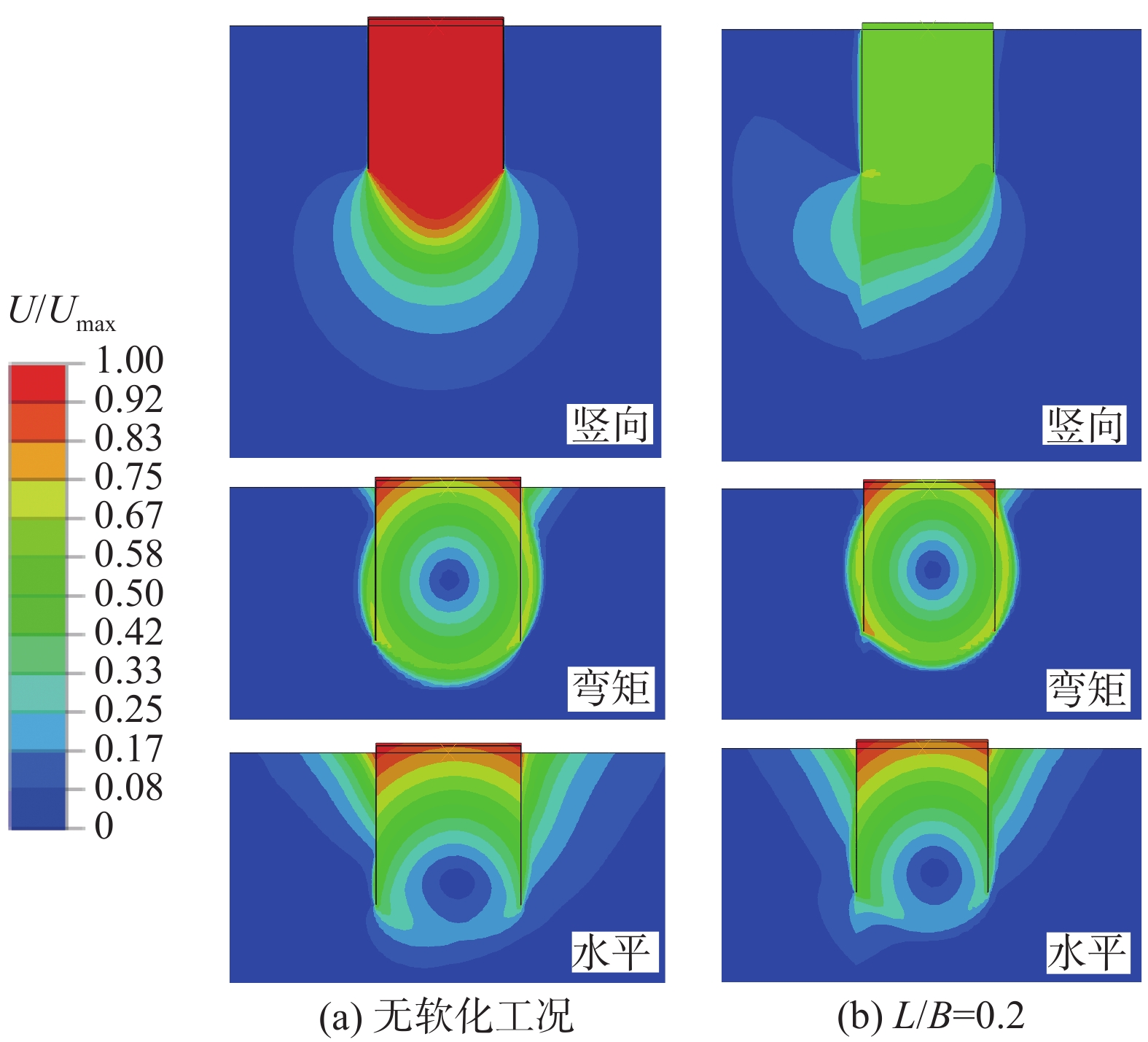
土体 工况 极限承载力 Hult/(MN) Mult/(MNm) Vult/(MN) soil#1 无软化 5.1 37.9 10.4 L/B = 0.2 4.2 29.7 8.2 L/B = 1 4.8 36.4 9.8 承载力折减系数α (0.82;0.96) (0.78;0.96) (0.73;0.94) soil#2 无软化 1.9 15.3 7.6 L/B = 0.2 1.5 11.5 5.5 L/B = 1 1.7 14.5 7.1 承载力折减系数α (0.79;0.89) (0.75;0.95) (0.72;0.93) 注:表中强度折减系数α=(a;b)分别对应工况(L/B = 0.2;L/B = 1) -
[1] 宋础, 刘汉中. 海上风力发电场开发现状及趋势 [J]. 电力勘测设计, 2006(2): 55-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9913.2006.02.014. SONG C, LIU H Z. The development and trend of wind power plant at sea [J]. Electric power survey & design, 2006(2): 55-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9913.2006.02.014.
[2] HOSSAIN M S, HU Y, RANDOLPH M F, et al. Limiting cavity depth for spudcan foundations penetrating clay [J]. Géotechnique, 2005, 55(9): 679-690. DOI: 10.1680/geot.2005.55.9.679.
[3] HOSSAIN M S, RANDOLPH M F. New mechanism-based design approach for spudcan foundations on single layer clay [J]. Journal of geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering, 2009, 135(9): 1264-1274. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.000 0054.
[4] MARTIN C M, HOULSBY G T. Combined loading of spudcan foundations on clay: laboratory tests [J]. Géotechnique, 2000, 50(4): 325-338. DOI: 10.1680/geot.2000.50.4.325.
[5] 潘泽华, 刘博, 刘东华. 可移动自升式平台的桩靴沉放安装研究 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10(1): 48-56. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.01.006. PAN Z H, LIU B, LIU D H. Research on the penetration of spudcan foundation for mobile jack-up platform [J]. Southern energy construction, 2023, 10(1): 48-56. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.01.006.
[6] ZHANG Y H, WANG D, CASSIDY M J, et al. Effect of installation on the bearing capacity of a spudcan under combined loading in soft clay [J]. Journal of geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering, 2014, 140(7): 459-477. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001126.
[7] 王凯, 武宗豪, 韩若朗, 等. 砂土中桩靴贯入深度对自升式风电安装船水平承载特性影响的试验研究 [J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10(4): 1-10. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.04.001. WANG K, WU Z H, HAN R L, et al. Model test study on the influence of the spudcan penetration depth on the horizontal bearing characteristics of jack-up vessel for wind turbine installation in sandy soil [J]. Southern energy construction, 2023, 10(4): 1-10. DOI: 10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2023.04.001.
[8] YUN G, BRANSBY M F. The horizontal-moment capacity of embedded foundations in undrained soil [J]. Canadian geotechnical journal, 2007, 44(4): 409-424. DOI: 10.1139/t06-126.
[9] 肖忠. 深埋式大圆筒防波堤稳定性分析的极限平衡法 [C]//中国力学大会-2017暨庆祝中国力学学会成立60周年大会论文集(A), 北京, 2017-08-13. 北京: 中国力学学会, 2017: 1220-1229. XIAO Z. Stability analysis of deeply embedded large cylindrical breakwater based on limit equilibrium method [C]//Chinese Congress of Mechanics-2017 Proceedings of the Conference Celebrating the 60th Anniversary of the Founding of the Chinese Society of Mechanics (A), Beijing, August 13, 2017. Beijing: The Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017: 1220-1229.
[10] FU D F, GAUDIN C, TIAN Y H, et al. Uniaxial capacities of skirted circular foundations in clay [J]. Journal of geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering, 2017, 143(7): 04017022. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001685.
[11] HUNG L C, KIM S R. Evaluation of undrained bearing capacities of bucket foundations under combined loads [J]. Marine georesources & geotechnology, 2014, 32(1): 76-92. DOI: 10.1080/1064119x.2012.735346.
[12] MANA D S K, GOURVENEC S, RANDOLPH M F. Experimental investigation of reverse end bearing of offshore shallow foundations [J]. Canadian geotechnical journal, 2013, 50(10): 1022-1033. DOI: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0428.
[13] XIE Y. Centrifuge model study on spudcan-pile interaction [D]. Singapore: National University of Singapore, 2009.
[14] THO K K, CHAN N, PAISLEY J. Comparison of coupled and decoupled approaches to spudcan-pile interaction [C]//Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics, London, 2015: 1317-1322. DOI: 10.1201/b18442-200.
[15] ZHANG H Y, LIU R, YUAN Y. Influence of spudcan-pile interaction on laterally loaded piles [J]. Ocean engineering, 2019, 184: 32-39. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.05.022.
[16] FAN Y F, WANG J H, FENG S L. Effect of spudcan penetration on laterally loaded pile groups [J]. Ocean engineering, 2021, 221: 108505. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108505.
[17] XIAO Z, LU Y M, WANG Y Z, et al. Investigation into the influence of caisson installation process on its capacities in clay [J]. Applied ocean research, 2020, 104: 102370. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2020.102370.
[18] ZHANG Y H, BIENEN B, CASSIDY M J, et al. The undrained bearing capacity of a spudcan foundation under combined loading in soft clay [J]. Marine structures, 2011, 24(4): 459-477. DOI: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2011.06.002.
[19] 戴笑如, 王建华, 范怡飞. 钻井船插桩CEL数值模拟中的若干问题分析 [J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(6): 2278-2286. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2142. DAI X R, WANG J H, FAN Y F. Issues of numerical simulation of the spudcan penetration based on CEL method [J]. Rock and soil mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 2278-2286. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2142.
[20] THO K K, LEUNG C F, CHOW Y K, et al. Eulerian finite-element technique for analysis of jack-up spudcan penetration [J]. International journal of geomechanics, 2012, 12(1): 64-73. DOI: 10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000111.
[21] HOSSAIN M. New mechanism-based design approaches for spudcan foundations in clay [D]. Perth: The University of Western Australia, 2008.
[22] 肖忠, 王琰, 王元战, 等. 桶间距对四桶吸力式基础各单向承载力的影响及最优间距的确定 [J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(10): 3603-3611. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.2277. XIAO Z, WANG Y, WANG Y Z, et al. Effect of bucket separation distance on bearing capacity of tetrapod bucket foundations and determination of optimal separation distance [J]. Rock and soil mechanics, 2018, 39(10): 3603-3611. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.2277.
[23] LIU R, YUAN Y, FU D F, et al. Geotechnical capacities of large-diameter cylindric foundations in clay under general loadings [J]. Applied ocean research, 2021, 117: 102951. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102951.
[24] SNAME. Recommended practice for site specific assessment of mobile jack-up units [M]. New Jersey: Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers, Technical and Research Bulletin5-5A, 2008: 64-109.
[25] EINAV I, RANDOLPH M F. Combining upper bound and strain path methods for evaluating penetration resistance [J]. International journal for numerical methods in engineering, 2005, 63(14): 1991-2016. DOI: 10.1002/nme.1350.
[26] ZHOU H, RANDOLPH M F. Penetration of full-flow penetrometers in rate-dependent and strain-softening clay [J]. Géotechnique, 2009, 59(2): 79-86. DOI: 10.1680/geot.2007.00164.




 下载:
下载: